Overview of available data sources in GIS Cloud
This portion of the documentation introduces types of data sources that can be included in a GIS Cloud project.
Topics in this guide
Learn how to upload existing data from your computer, from a PostGIS database, transfer data from desktop GIS software, or connect to certain web services and understand the full benefit of our cloud-based data organization.
GIS Cloud data management helps you keep things simple and organized through the File Manager, Database Manager and Datasource Manager.
Supported data sources
- File Manager – Upload files from the local computer
- Database – Load spatial data from the database
- Web Feature Service – Add features as an editable version of data that one would view via WMS
- Web Map Services – Add maps as a standard protocol for serving georeferenced map images over the Internet that are generated by a map server using data from a GIS database
- Web Map Tile Service – Add data as a pre-rendered georeferenced map tiles over the Internet
- Tile Map Service – Loads rasters of maps like Open Street Maps, Mapbox or Bing; these can serve as a basemap
- Mobile Data Collection – Collect data from your mobile device
- GIS Cloud Maps – Load maps from GIS Cloud database
- Esri Arcmap – Upload shapefiles with our free extension for Arcmap
- QGIS – Upload files with our free extension for QGIS
- Datasources – add data which was shared with you from another GIS Cloud account
How to find out which layer source you’re using
Once your layers are added to the map, you can easily check their source and other technical “metadata” in the Layer Properties, or, even quickly, a portion of them can be found by hovering over the wanted layer in the Layer List.
In Layer Properties (General tab) under Source and More info the following information can be obtained: Layer name, Layer ID, Layer data source (type, name and ID), geometry type, number of features, projection, units, bounds, attributes, and many other options.
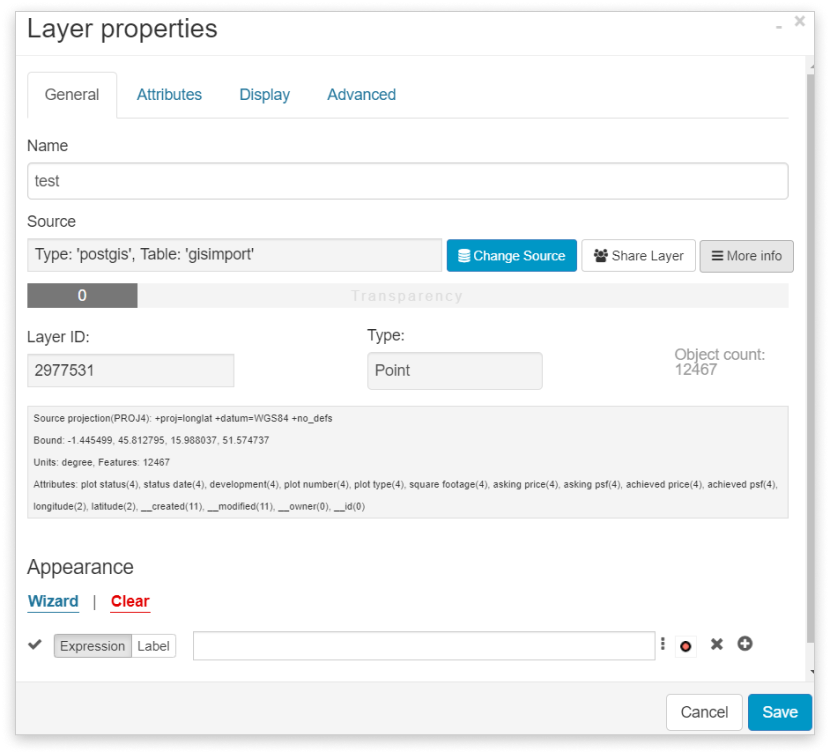
Hovering over the wanted layer in the Layer list, an info window appears containing a few basic information as well. This information contains the Layer ID, Layer name, Layer data source (type, name, and ID).
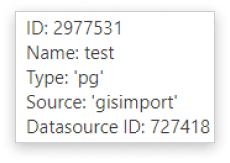
Depending on the upload source the type can be: ‘file’ – file from the File Manager, ‘postgis’ or ‘pg’ – table from the database, ‘tile’ – basemap, ‘wfs’/‘wms’/’wmts’ as web services and ‘gcmap’.
The layer’s source can also be changed in Layer Properties, unless it is an MDCP project. This feature is quite useful if you’re editing data in an external (GIS) software and you need to update the changes in GIS Cloud. Learn more about updating or changing layer source.
Besides adding data from external sources to your account, you can create new datasets by yourself, either through the Map Editor or from the field using Mobile Data Collection.
Feel free to check out our other data management guides:
